Introduction
Peatlands are fascinating ecosystems that have formed over thousands of years, playing a crucial role in our environment and biodiversity. As a product of the unique interactions between living organisms and their surroundings, they are classified into natural and artificial ecosystems. In this article, we will explore peatlands in detail, their significance, the threats they face, and the importance of their conservation.
What Are Peatlands?
Peatlands are wetland areas where accumulation of organic material, primarily dead plant matter, takes place over long periods. Typically found in lowlands, peatlands can cover vast areas and are recognized for their unique soil composition and ecological functions.
Formation of Peatlands
- Timeline: Peatlands have formed over 10,000 to 40,000 years through the gradual decomposition of plant materials near water bodies like lakes.
- Process: As plants die, they decay slowly in waterlogged conditions, creating thick layers of wet, organic-rich soil known as peat.
- Characteristics: Peatlands resemble sponges, capable of absorbing large quantities of water, up to 13 times their weight, and play a critical role in water regulation.
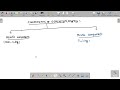
Types of Ecosystems
Peatlands can be classified into two primary ecosystems: natural and artificial, with natural peatlands being the focus of our discussion.
Natural Ecosystems
- Aquatic Ecosystem: Includes wetlands, lakes, and rivers around peatlands which host diverse aquatic life. Learn more about these vital interactions in our summary on Understanding Ecosystem Components: A Comprehensive Guide.
- Terrestrial Ecosystem: Comprised of forests and other land areas surrounding peatlands, supporting diverse life forms including endangered species.
Artificial Ecosystems
- Human-Made: Examples include plantations, ponds, and other environments created through human intervention.
Biodiversity in Peatlands
Peatlands are home to a rich biodiversity, supporting numerous plant and animal species:
- Flora: Species like maranti, pulai, palm, orchids, and various herbs thrive in peatland environments.
- Fauna: Endangered species such as the Sumatran tiger, rhinos, and a multitude of bird species find refuge in these habitats. For more on the effects of habitat loss, see Understanding Deforestation: Causes, Effects, and Solutions.
- Aquatic Life: Peatland waters are rich in organic substances, supporting various fish, snails, shrimps, and crabs.
Peatlands and Agriculture
Peatlands are not only ecological reserves but also play a vital role in agriculture:
- Farming: Cultivation of crops like pineapple and rubber plants.
- Fishing: Supports local aquaculture; valuable seafood such as snails, shrimps, and crabs thrive in peatland waters.
The Role in Climate Regulation
Peatlands are crucial for climate stability:
- Carbon Reservoirs: Peat soils in Indonesia, which contain the largest peatlands in the world, store an estimated 57 to 60 billion metric tons of carbon. To learn more about the global implications of carbon emissions, read The Urgent Call for Climate Action: Our Responsibility to Save Earth.
- Flood Mitigation: Their sponge-like quality allows them to absorb excess rainwater, thus playing a role in flood prevention.
Threats to Peatlands
Despite their importance, peatlands face significant threats:
- Deforestation and Draining: Clearing for agriculture and urban development reduces their area.
- Fires: Peatlands are susceptible to fires, especially during dry seasons, leading to immense carbon release and habitat destruction. Explore sustainable practices in Understanding Clear Cutting and Sustainable Forestry Practices.
- Pollution: Activities surrounding peatlands can introduce toxic substances, affecting water quality and biodiversity.
Consequences of Damaging Peatlands
The degradation of peatlands can have severe implications:
- Water Absorption Loss: Damaged peatlands lose their ability to retain water, leading to increased flooding.
- Biodiversity Decline: Aquatic species struggle to survive as the water quality deteriorates, affecting local fisheries and ecosystems.
- Climate Change Acceleration: The release of stored carbon contributes to global warming, leading to rising temperatures that can severely impact Earth's climatic balance.
Conclusion
Understanding the vital role of peatlands is essential for their conservation. Protecting these ecosystems not only supports biodiversity but also helps regulate our climate and manage water resources. It is imperative for individuals and communities to take conscious steps towards preserving our peatlands, recognizing their immense value.
Call to Action
What measures will you take to support and conserve your local environment? Every small action can contribute to the global effort of protecting peatlands and ensuring the survival of our planet's biodiversity.
[Music] ecosystem is a mutual relationship between living things and their
environment ecosystem is classified into two types natural ecosystem natural ecosystem is an ecosystem that is formed
naturally for example Forest River and sea artificial ecosystem artificial
ecosystem is manufactured by human for example pedi Plantation and pond natural ecosystem is classified
into two types aquatic ecosystem such as sea swamp and Lake terrestrial ecosystem such as
Forest meow and pit [Music] lands
what is pit land pit land had been formed from 10 to 40,000 years ago as plants around the lake die they
gradually form wet and thick [Music] soil water in the pit lands slow down
the microorganism to decompose organic materials such as residual Roots stem and Dead
Leaves as a result the organic piles decompose faster so the pit land contains massive
organic substances this Thousand Years process results the pit land that we know
today Indonesia has the largest pit LS in the world which spreads in Sumatra cantan
Papua normally lands are found in lowlands around the coast with total area of 20 million hectar or 10.8% of
total indonisia land area pit LS and its watercolor are blackish Brown that's why it is often
cul like water even though the color is dark the river around the pet lands contain
massive organic [Music] substances there are plenty of rivers in
the pet lands even though the river streams are dark colored there are numbers of fishes snails shrimps and
crafts live in [Music] there bit lands are also a home to
arrange kinds of IND dangered animals such as aragan tiger Rhino and various species of
birds because of its unique ecosystem hundreds of plants such as maranti pulai palm Orchid and some herbs can be found
in pit [Music] lands bit lands are great for farming
and fishing some plants in the farming and agriculture areas that can be cultivated
in bit lands or pineapple and rubber plants for fishing and aquaculture animals are snail shrimp and
crab [Music] pit land's characteristic is similar to
sponge when pit land's dry it absorbs a large amount of water 13 times its own weight similar to sponge after pit LS
absorb water the excess water will be released around the permeable soil that's why pit land sit the key to
anticipate flood and to maintain more Supply pit land soil in Indonesia plays the most significant role in the world
as it absorbs around 57 to 60 billion metric D carbon this means that the soil under
pit LS area has a numerous carbon Reservoir this carbon Reservoir can be released to the air while the land is
burnt and its land surface is exposed directly under the sun continually if all this carbon Reservoir
is Rel least at the same time to the air the Earth temperature will be hotter and can raise up to
[Music] 4° the unrestricted beat lands often cause
issues in order to clear pit lands human often burn the ticket what will happen if pit lands is
damaged the damaged pit lands cannot absorb water therefore it floods as the Heavy Rain
occurs when flood occurs the acidic water extracted from pit lands will be sponged up to freshwater rivers around
pits the fishes that live in those River can hardly survive so they migrate to fresher water
Rivers as the fishes are fewer the fisherman are difficult to fish the damaged pit soil can easily
Carried Away by the stream and pass into the river as a result the rivers will be
shallow or often to have sedimentation if this happens continually the rofs will fade and there
will be no [Music] water during dry season the dry land
will easily get burnt due to lack of water reservoir bit land fors are difficult to
be extinguished as the land is acident and the fireb burs plants quickly as it passes underneath the pit land soil as
well the smoke produced by burning pit lands is massive and highly dangerous for human as it could cause lungs
diseases the animals that live at burn pit land would lose their habitat and many could also die because of smoke or
getting [Music] burnt and the carbon on your the burning
pit land soil can be released to the air and it will raise the Earth temperature it's horrifying isn't
it so what do you think now that we know the importance of pit LS we should conserve and maintain the pit LS
wisely we have to keep an eye on our surroundings as well not only the pit lands so that we can value and conserve
our environment wisely what will you do to preserve your [Music]
environment
Heads up!
This summary and transcript were automatically generated using AI with the Free YouTube Transcript Summary Tool by LunaNotes.
Generate a summary for freeRelated Summaries

Understanding Peatlands: The Vital Ecosystem
Explore the importance of peatlands as a unique ecosystem and their role in environmental conservation.

Understanding Deforestation: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
Explore the causes and impacts of deforestation on ecosystems and climate change, and discover solutions to combat this global issue.
Understanding Ecosystem Components: A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the intricate components of ecosystems, their functions, and significance in nature.

The Urgent Call for Climate Action: Our Responsibility to Save Earth
Explore the critical state of our environment and what we can do to combat climate change.

Understanding Clear Cutting and Sustainable Forestry Practices
Explore the contrasts between clear cutting and sustainable forestry, focusing on their effects on ecosystems and resource management.
Most Viewed Summaries

Kolonyalismo at Imperyalismo: Ang Kasaysayan ng Pagsakop sa Pilipinas
Tuklasin ang kasaysayan ng kolonyalismo at imperyalismo sa Pilipinas sa pamamagitan ni Ferdinand Magellan.

A Comprehensive Guide to Using Stable Diffusion Forge UI
Explore the Stable Diffusion Forge UI, customizable settings, models, and more to enhance your image generation experience.

Pamamaraan at Patakarang Kolonyal ng mga Espanyol sa Pilipinas
Tuklasin ang mga pamamaraan at patakaran ng mga Espanyol sa Pilipinas, at ang epekto nito sa mga Pilipino.

Mastering Inpainting with Stable Diffusion: Fix Mistakes and Enhance Your Images
Learn to fix mistakes and enhance images with Stable Diffusion's inpainting features effectively.

Pamaraan at Patakarang Kolonyal ng mga Espanyol sa Pilipinas
Tuklasin ang mga pamamaraan at patakarang kolonyal ng mga Espanyol sa Pilipinas at ang mga epekto nito sa mga Pilipino.

